OXAliplatin
View Brand InformationWhat is OXAliplatin?
Approved To Treat
Related Clinical Trials
Summary: GEMINI-PeriOp GC study will assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK) and preliminary anti-tumor activity of novel agents or novel combinations as perioperative treatment in participants with locally advanced resectable gastric, gastroesophageal junction (GEJ), or esophageal adenocarcinoma who have not received previous treatment for the disease.
Summary: This ComboMATCH patient screening trial is the gateway to a coordinated set of clinical trials to study cancer treatment directed by genetic testing. Patients with solid tumors that have spread to nearby tissue or lymph nodes (locally advanced) or have spread to other places in the body (advanced) and have progressed on at least one line of standard systemic therapy or have no standard treatment t...
Summary: The main purpose of this study is to assess safety \& tolerability and antitumor activity of LY3962673 as monotherapy and in combination with other chemotherapy agents in participants with KRAS G12D-mutant advanced solid tumor types. The study is expected to last approximately 5 years.
Related Latest Advances
Brand Information
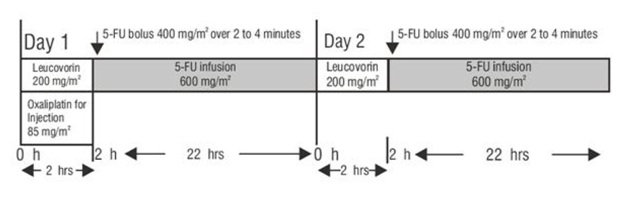
After reconstitution in the original vial, the solution may be stored up to 24 hours under refrigeration [2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F)]. After final dilution with 250 to 500 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, the shelf life is 6 hours at room temperature [20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F)] or up to 24 hours under refrigeration [2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F)].Oxaliplatin for injection is not light sensitive.
Oxaliplatin for injection is incompatible in solution with alkaline medications or media such as basic solutions of 5-fluorouracil) and must not be mixed with these or administered simultaneously through the same infusion line. The infusion line should be flushed with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP prior to administration of any concomitant medication.Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration and discarded if present.
Needles or intravenous administration sets containing aluminum parts that may come in contact with oxaliplatin for injection should not be used for the preparation or mixing of the drug. Aluminum has been reported to cause degradation of platinum compounds.
- Anaphylaxis and Allergic reactions
- Neuropathy
- Severe Neutropenia
- Pulmonary Toxicities
- Hepatotoxicity
- Cardiovascular Toxicities
- Rhabdomyolysis
The following table provides adverse reactions reported in the adjuvant therapy colon cancer clinical trial [see Clinical Studies (14)] by body system and decreasing order of frequency in the oxaliplatin for injection and infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm for events with overall incidences ≥ 5% but with incidences <1% NCI grade 3/4 events.
Table 4 - Adverse Reactions Reported in Patients with Colon Cancer receiving Adjuvant Treatment (≥ 5% of all patients, but with <1% NCI Grade 3/4 events)
The incidence of Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia was 2% in adjuvant patients with colon cancer. In patients treated for advanced colorectal cancer the incidence of Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia was 3 to 5%, and the incidence of these events was greater for the combination of oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin over the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin or 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin control groups. Grade 3/4 gastrointestinal bleeding was reported in 0.2% of adjuvant patients receiving oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin. In the previously untreated patients, the incidence of epistaxis was 10% in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm, and 2% and 1%, respectively, in the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin or irinotecan plus oxaliplatin for injection arms.
Neutropenia
Neutropenia was frequently observed with the combination of oxaliplatin for injection and 5-
fluorouracil/leucovorin, with Grade 3 and 4 events reported in 29% and 12% of adjuvant patients with colon cancer, respectively. In the adjuvant trial, 3 patients died from sepsis/neutropenic sepsis. Grade 3 and 4 events were reported in 35% and 18% of the patients previously untreated for advanced colorectal cancer, respectively. Grade 3 and 4 events were reported in 27% and 17% of previously treated patients, respectively. In adjuvant patients the incidence of either febrile neutropenia (0.7%) or documented infection with concomitant grade 3/4 neutropenia (1.1%) was 1.8% in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm. The incidence of febrile neutropenia in the patients previously untreated for advanced colorectal cancer was 15% (3% of cycles) in the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm and 4% (less than 1% of cycles) in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm. Additionally, in this same population, infection with grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was 12% in the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin, and 8% in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination. The incidence of febrile neutropenia in the previously treated patients was 1% in the 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm and 6% (less than 1% of cycles) in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm.
Gastrointestinal
In patients receiving the combination of oxaliplatin for injection plus infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin for adjuvant treatment for colon cancer the incidence of Grade 3/4 nausea and vomiting was greater than those receiving infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin alone (see table). In patients previously untreated for advanced colorectal cancer receiving the combination of oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin, the incidence of Grade 3 and 4 vomiting and diarrhea was less compared to irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin controls (see table). In previously treated patients receiving the combination of oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin, the incidence of Grade 3 and 4 nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mucositis/stomatitis increased compared to 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin controls (see table).
The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions in the previously untreated and previously treated patients appears to be similar across cycles. Premedication with antiemetics, including 5-HT3 blockers, is recommended. Diarrhea and mucositis may be exacerbated by the addition of oxaliplatin for injection to 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin, and should be managed with appropriate supportive care. Since cold temperature can exacerbate acute neurological symptoms, ice (mucositis prophylaxis) should be avoided during the infusion of oxaliplatin for injection.
Dermatologic
Oxaliplatin for injection did not increase the incidence of alopecia compared to 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin alone. No complete alopecia was reported. The incidence of Grade 3/4 skin disorders was 2% in both the oxaliplatin for injection plus infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin and the infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin alone arms in the adjuvant colon cancer patients. The incidence of hand-foot syndrome in patients previously untreated for advanced colorectal cancer was 2% in the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm and 7% in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm. The incidence of hand-foot syndrome in previously treated patients was 13% in the 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm and 11% in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm.
Intravenous Site ReactionsExtravasation, in some cases including necrosis, has been reported.
Injection site reaction, including redness, swelling, and pain, has been reported.
Anticoagulation and HemorrhageThere have been reports while on study and from post-marketing surveillance of prolonged prothrombin time and INR occasionally associated with hemorrhage in patients who received oxaliplatin for injection plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin while on anticoagulants. Patients receiving oxaliplatin for injection plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin and requiring oral anticoagulants may require closer monitoring.
RenalAbout 5 to 10% of patients in all groups had some degree of elevation of serum creatinine. The incidence of Grade 3/4 elevations in serum creatinine in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5- fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm was 1% in the previously treated patients. Serum creatinine measurements were not reported in the adjuvant trial.
Hepatic
Hepatotoxicity (defined as elevation of liver enzymes) appears to be related to oxaliplatin for injection combination therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. The following tables list the clinical chemistry changes associated with hepatic toxicity occurring in ≥5% of patients, based on adverse reactions reported and NCI CTC grade for adjuvant patients and patients previously untreated for advanced colorectal cancer, laboratory values and NCI CTC grade for previously treated patients.
Table 12 - Adverse Hepatic Reactions in Patients with Stage II or III Colon Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Therapy (≥5% of patients)
The incidence of thromboembolic events in adjuvant patients with colon cancer was 6% (1.8% grade 3/4) in the infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm and 6% (1.2% grade 3/4) in the oxaliplatin for injection and infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combined arm, respectively. The incidence was 6 and 9% of the patients previously untreated for advanced colorectal cancer and previously treated patients in the oxaliplatin for injection and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm, respectively.
- To expect side effects of oxaliplatin for injection, particularly its neurologic effects, both the acute, reversible effects and the persistent neurosensory toxicity. Patients should be informed that the acute neurosensory toxicity may be precipitated or exacerbated by exposure to cold or cold objects.
- To avoid cold drinks, use of ice, and should cover exposed skin prior to exposure to cold temperature or cold objects.
- Of the risk of low blood cell counts and to contact their physician immediately should fever, particularly if associated with persistent diarrhea, or evidence of infection develop.
- To contact their physician if persistent vomiting, diarrhea, signs of dehydration, cough or breathing difficulties occur, or signs of allergic reaction appear.
- To exercise caution when driving and using machines. No studies on the effects of the ability to operate cars and machines have been performed; however, oxaliplatin treatment resulting in an increase risk of dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and other neurologic symptoms that affect gait and balance may lead to a minor or moderate influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
- Of the potential effects of vision abnormalities, in particular transient vision loss (reversible following therapy discontinuation), which may affect patients' ability to drive and use machines.
Vial Label
Carton Label
OXALIPLATIN FOR INJECTION, USP
100 mg/Vial
Cytotoxic Agent
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
SINGLE DOSE VIAL
Lyophilized
Must be reconstituted and diluted before use
Vial Label
Carton Label
